
ICO vs. IPO – Modern Finance Explained By Professionals
The latest cryptocurrency technology has given us an entirely new investment option: the Initial Coin Offering (ICO). If you have some money to invest, you can go with a well-known, IPO-based business or fund one of the young startups via an ICO. What are the differences between them and the one you would prefer?
The first and most important distinction is that an IPO is typically reserved for well-established businesses, while an ICO is more suited to the young and risky. The first has a well-known, profitable company, a strong bank account, and a track record of success. The second has none of the above characteristics; he might be the next hotshot, but everyone might forget his brilliant idea in a year.
The Differences Between the Two
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
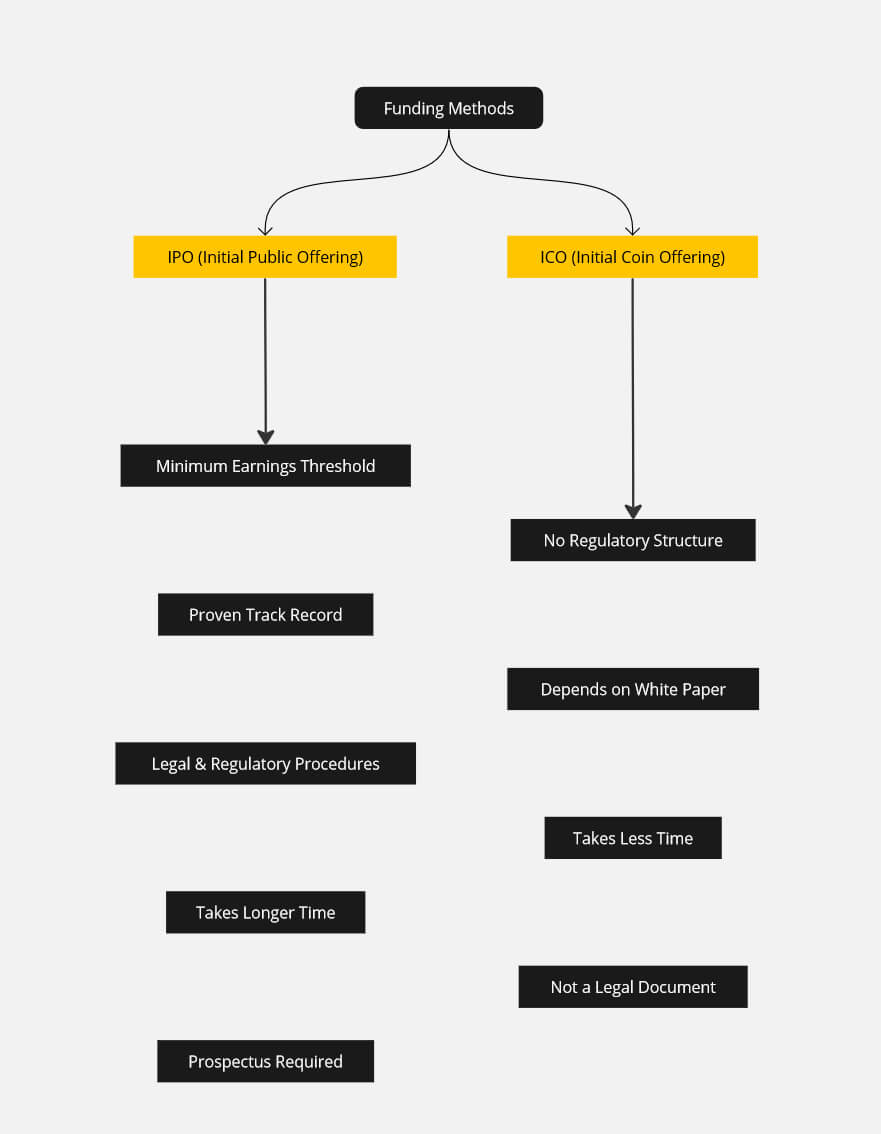
Before launching an IPO, a company must meet various conditions, including meeting a minimum earnings threshold and having a proven track record. Due to the need for legal and regulatory procedures, traditional IPO issuance will take a long time. A prospectus is another prerequisite.
The prospectus is a legal statement of the company’s intention to sell its stock to the general public. It must include key details about the company and its upcoming IPO to help prospective investors make an informed decision. So, to prepare for an IPO, you’ll need time, legal counsel, and financial resources.
Initial Coin Offering (ICO)
Since ICOs are exempt from any regulatory structure or legal protocol, the vast majority of them have no track record and depend solely on a white paper to support their project.
The whole ICO procedure takes far less time. A white paper is usually issued with an ICO project, but unlike an IPO, it has no set format.
Please keep in mind that a piece of paper like this is not considered a legal document in certain nations. So, for an ICO, you’ll need programmers as well as access to the Internet. Further discussion of it is not necessary.
Investing in ICO vs. IPO
IPO
Investors require an initial public offering. It is relatively simple to invest in a business based in your own country. If you want to invest in a foreign business, you’ll almost certainly need to use a broker’s services.
ICO
This is the most enjoyable part. To begin investing in an ICO, all you need is a connection to the Internet. Users can purchase any company’s tokens from any country.
Some US ventures that are classified as securities are an exception to this rule. This project is not open to those residing in the US because it would require IPO-style documentation, which goes against the whole point of an ICO.

Benefit for Investors – ICO vs. IPO Advantages
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
Stocks purchased in an initial public offering (IPO) reflect an interest in the company’s potential earnings. Dividends are paid to shareholders annually, based on the company’s performance during the year. Another way to make money is to buy stock early and then sell it as the price increases.
The most important thing to note is that coins do not grant project ownership. Investors in the coins can reap future benefits in various ways, depending on how the coin is designed. It may be a set price at which you can purchase or sell it, a sum of money you can receive if the company makes more money than expected, or the right to visit their offices and eat in their dining room whenever you want. Whatever it is, it’s written on the project’s white paper.
Can we conclude from this that an IPO is more reliable than an ICO? Despite what might seem to be the case, it is not. Despite all of the documentation, audits, and legal provisions, the company might still go bankrupt, wiping out your investment.
On the other hand, if you pick a successful ICO project, it could be a very lucrative investment with minimal red tape. It is critical to fully understand all available resources to ensure a project that is worth your money in both cases.
Advantages and Disadvantages of an ICO
The terms initial coin offering (ICO) vs. initial public offering (IPO) sound similar, but they are not the same. Both have their collection of advantages and disadvantages. Still, in today’s business world, where businesses tend to maintain more leverage over their operations while attracting more investors, ICOs are more appealing due to their major advantages. Let’s go through the main benefits of an ICO that are attracting a lot of potential investors.
- Transaction costs are lower
The ICO price is often lower since transactions are made in cryptocurrencies. Trading between individuals is easy, and trading on a centralized crypto exchange will cost you just 0.1 to 0.3 percent.
Smart contracts remove the need for intermediaries, lowering service delivery costs. Furthermore, there are no administrative expenses associated with buying and selling. Stock transactions, on the other hand, are extremely costly, with hefty intermediary fees.
- Trading options are available 24 hours a day, seven days a week
Cryptocurrency exchanges are open 24 hours a day, seven days a week. As a result, you can purchase ICOs whenever you like. However, stock exchanges are only available for a limited time.
- Discretion
Anyone can see a cryptocurrency transaction because it is highly transparent. This lowers the error rate and removes any potential for a disagreement. One of the most convincing advantages of an ICO is its transparency.
- It’s simple to get started with funding
A small business or a startup may use an initial coin offering (ICO) to raise funds quickly and easily. Small businesses can find the procedure simpler because it is less difficult and does not require legal documents. Everyone can make money with ICOs.
- full discretion over who you sell your ICO to
- More rapid settlement
Cryptocurrency transactions are completed in a matter of minutes. Stock markets, on the other hand, typically settle in a few days. This enables both ICO issuers and investors to complete transactions quickly.
- There is no oversight
Due to the lack of regulatory bodies for cryptocurrencies, ICO transactions and exchange processes are unregulated. As a result, there is a greater sense of empowerment and accessibility.
- International transactions initial coin offerings
(ICOs) are international transactions subject to local regulatory restrictions. Any investor may gain access to blockchain technologies regardless of their location. This does not require any extra charges. In the case of a stock exchange, though, an overseas exchange is more expensive.
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
The IPO (Initial Public Offering) is a method of taking a private company public. If you want to be listed on a stock exchange, you must go through a structured process. So, what exactly is an Initial Public Offering? Simply put, an IPO is when you sell the company’s shares to the public and raise money.
It’s a significant move for your company because it will give you access to a large sum of money and make it easier to develop and expand. As a result, IPOs are a great idea, mainly if you’ve achieved a high degree of maturity and financial stability.
Prerequisites
You must file a declaration with the Securities and Exchange Commission to register an IPO (SEC). Disclosure should include a prospectus with risk factors and financial statements that prospective investors would want to see.
Investor Expectations
Potential investors will search S-1 forms filed with the SEC to learn about companies and company offers, that are about to go public. They must register with a brokerage firm if they find an IPO they want to invest in.
The firm would almost always demand that they fulfill such transaction or net worth conditions. According to Fidelity, an investor must have either $100,000 or $500,000 in household assets or at least 36 trades per year before investing in IPOs.
How Does it Work?
You’ll inform the US government if your company plans to go ahead with an IPO. Then you’ll generate investor interest and wait for the price to be set by underwriters. Your privately held company will no longer be privately held if your company successfully files for an IPO. Investors who purchase the company’s stock will become the new owners.
The Benefits
The following are the most significant advantages of IPOs:
- Increased Business Opportunities: When you go public, you open yourself to people and organizations that may not otherwise know about you. This could open up more business opportunities for you and improve your chances of success.
- Attract Talent: If you collect funds from an IPO, you can attract top talent by providing stock options and other attractive benefits.
- Improves Corporate Reputation: In general, the public respects public corporations more than private companies. You will be seen as larger and more competitive than any of your private rivals if you become a publicly-traded company.
Potential Negative Consequences
IPOs have several drawbacks, including:
- Time: The length of the process is perhaps the most significant drawback of an IPO. It’s not unusual for the procedure to take six months or longer. This is since you must follow a variety of legal procedures before you can sell your stock.
- Expensive: If you go the IPO path, you’ll have to pay fees for underwriting, filing, reporting, and other services. Unfortunately, this can easily add up and put a strain on your finances.
- Pressure to Perform: Since your results will be announced every quarter, you will feel pressure to perform well and keep your investors satisfied.
The Final Question
Which would you choose to pursue—an ICO or an IPO—in that situation? The response is that it depends on your specific business and long-term objectives. An ICO could be the best choice if you are a startup owner looking for financing to get your business off the ground. It will provide you with the funds you need to purchase equipment, recruit staff, sell your products, and do everything else you need to get your business off the ground.

However, if your company has been around for a while, an IPO could be a better option. This is especially true if it is financially stable and wants to switch from private to public ownership. An IPO will help you expand and develop your company. Furthermore, it will help you establish a solid reputation and open doors to a variety of opportunities.
Make sure you understand how an ICO or IPO operates, as well as the benefits and drawbacks that come with it before you pick one. This way, you’ll be able to make an educated decision that will help your company prosper for years to come.
-
Support
-
Platform
-
Spread
-
Trading Instrument




