
How to Find Key Levels in Stocks: A Comprehensive Guide
You must know how to find key stock levels when trading on a stock market.
Identifying key stock levels is essential for effective trading as they serve as critical points influencing price movements.
Knowing how to locate and interpret these levels provides traders valuable insights, aiding in informed decision-making and enhancing overall market navigation.
This article explores the significance of identifying key stock levels and offering insights and strategies to help you make informed decisions and navigate the dynamic stock market landscape.
What Are Key Levels in Trading?
Key levels in trading are specific price points on charts that traders consider significant for the entry and exit of trades.
These levels often act as barriers, where the price of a stock tends to pause or reverse. They include support and resistance levels, Fibonacci retracement levels, and other pivotal points identified through technical analysis.
Why Are Key Levels Important in Trading?
Key levels are crucial because they help traders make informed decisions based on historical price action and volumes.
These levels can indicate potential price breaks or reversals, offering opportunities for profitable trades. Understanding key levels also aids in risk management, allowing traders to set more accurate stop-loss and take-profit orders.
8 Techniques to Find Key Levels in Stock Trading
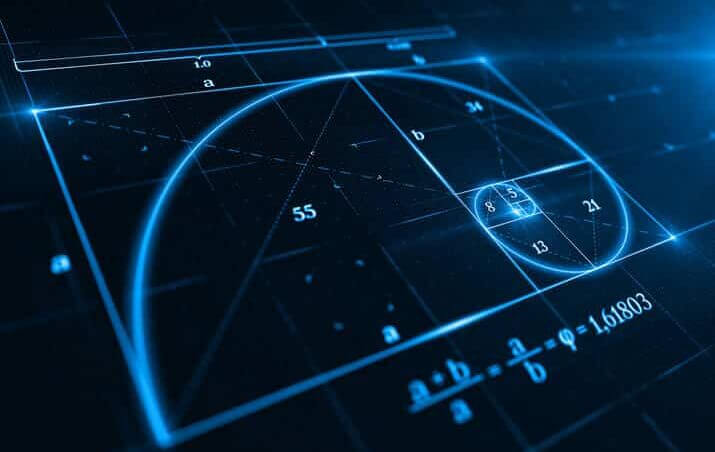

1. Fibonacci Retracement Levels
Fibonacci retracement levels are popular among traders for identifying potential support and resistance.
By drawing horizontal lines across a chart at the key Fibonacci ratios (23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100%), traders can pinpoint areas where the market may pause or reverse.
These levels are derived from the Fibonacci sequence, a series of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones.
The theory behind using Fibonacci levels is that markets tend to retrace a predictable portion of a move before continuing in the original direction.
2. Horizontal Lines
Horizontal lines are straightforward yet powerful tools for marking support and resistance zones.
Traders identify significant price points where the market has historically faced upward or downward pressure and draw horizontal lines at these levels. Consequently, these zones act as barriers where the price may struggle to break through.
Identifying these areas helps traders anticipate potential market movements and make informed entry and exit point decisions.
3. Round Numbers
Round numbers, such as 10, 20, 50, 100, etc., often serve as psychological barriers in the market.
Traders and investors pay close attention to these levels, making them self-fulfilling prophecies as areas of support or resistance.
The human brain tends to gravitate towards simplicity. Therefore, round numbers provide a clear and memorable price level around which trading decisions are often made.
4. Moving Averages
Moving averages are vital indicators for determining the market’s direction. These lines smooth out price data to reveal the underlying trend by averaging the closing prices over a specific period.
Key moving averages, such as the 50-day and 200-day, are particularly watched by traders. A stock above a moving average might indicate a bullish trend, while falling below could suggest a bearish trend.
Additionally, moving averages themselves can act as dynamic support or resistance levels.
5. Volume
Volume measures the number of shares traded in a stock or market during a given period. High volume at a specific price level indicates a strong interest in buying or selling.
When a key level coincides with high volume, it reinforces that level’s significance, suggesting that many traders are willing to support or oppose the price movement at this point.
6. Trend Lines/Trend Channels
Trend lines are drawn by connecting two or more price points, extending into the future to act as support or resistance. When prices break through these lines, it may signal a change in trend direction.
Similarly, trend channels are formed by drawing parallel lines above and below a trend line, creating a channel where the price is expected to move. These tools help traders visualize the trend’s strength and potential reversal points.
7. Pivot Points
Pivot points are calculated based on the previous trading day’s high, low, and close. They identify potential support and resistance levels for the current trading session.
Day traders widely use this technique to make quick, informed decisions. Pivot points offer a mathematical approach to trading, providing clear levels for monitoring market movements.
8. Previous Day’s High or Low and All-time High/Low
The highs and lows of the previous trading session and all-time highs and lows are crucial markers for traders.
These levels represent points where the market has previously made significant turns or shown strong resistance or support. Traders monitor these levels closely for signs of breakouts or reversals, leveraging historical price action to forecast future movements.
Understanding and utilizing these tools and techniques allow traders to navigate the stock market more precisely.
By identifying key levels, traders can optimize their strategies, improve their risk management, and enhance their potential for success in the volatile world of stock trading.
Trading Breakouts with Key Levels
Trading breakouts involve identifying when a stock’s price moves beyond a defined key level, such as a resistance or support line, with increased volume.
This movement can indicate a new trend’s beginning, offering traders an opportunity to enter a trade early in its formation. The rationale behind breakout trading is that key levels act as barriers that, when broken, signify a strong market sentiment shift.
For instance, if a stock has been trading in a tight range and suddenly breaks above a well-established resistance level, this could suggest that buyers have overpowered sellers, potentially leading to a bullish trend.
Traders looking to capitalize on breakouts will set buy orders just above resistance levels or sell orders just below support levels, anticipating the price movement’s continuation in the breakout direction.
However, successful breakout trading requires confirmation. Volume plays a crucial role here; a significant increase in trading volume typically accompanies a genuine breakout. This increase confirms the strength and commitment behind the price move. Without this confirmation, traders risk falling into a “false breakout,” where the price briefly surpasses a key level only to revert to its previous range.
Trading Reversals with Key Levels
Conversely, trading reversals with key levels focus on identifying potential points where the prevailing trend might change direction.
Key levels are significant in this strategy because they can highlight areas where the market sentiment may shift from bullish to bearish or vice versa.
For example, if a stock approaching a strong resistance level fails to break through and instead starts to decline, it might indicate a reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend.
When trading reversals, traders look for price action signals such as pin bars, engulfing patterns, or other candlestick formations that suggest a change in direction near these key levels. Additionally, divergence between the price and momentum indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) can further validate reversal signals.
In reversal trading, waiting to confirm trend change before executing trades is essential.
This might mean waiting a few periods to ensure the price does not resume its previous trend. Setting stop-loss orders near the key level can help manage the risk if the expected reversal does not materialize.
Both breakout and reversal trading strategies require a deep understanding of key levels and market psychology.
They demand discipline in entry and exit strategies and a comprehensive risk management plan to effectively navigate the complexities of market movements.
Advanced Techniques for Trading Key Levels

Multiple Time Frame Analysis
Multiple time frame analysis involves examining stock price movements across different time frames to confirm key levels and trading signals.
Traders can align their strategies with the broader market direction by analyzing long-term trends on weekly or monthly charts and then zooming into daily or hourly charts for entry points.
This approach offers a more comprehensive view, ensuring that trades based on key levels are in sync with micro and macro trends.
Price Action Analysis
Price action analysis focuses on the raw price movements of a stock without relying on indicators.
Traders make informed decisions by looking for patterns like hammer candles, shooting stars, or inside bars near key levels.
Traders can predict potential breakouts or reversals by understanding how prices behave at these critical points. Price action provides insight into market sentiment, indicating whether key levels will hold or break.
Confluence of Key Levels
Confluence occurs when multiple indicators or analyses point to the same key level, strengthening its significance.
For example, a key level that coincides with the 61.8% Fibonacci retracement level and a long-term moving average might offer a robust trading signal.
Traders seek out these confluences, which often indicate stronger support or resistance levels, which provides greater confidence in potential trades.
Volatility Analysis
Volatility analysis helps traders understand how much a stock’s price might move in the future. Tools like the Average True Range (ATR) or Bollinger Bands gauge market volatility and indicate how likely a price will reach or break through a key level.
High volatility periods may see more significant price movements, making adjusting strategies and stop-loss orders crucial.
Pattern Recognition
Pattern recognition involves identifying common chart patterns, such as triangles, flags, or heads and shoulders, that occur near key levels.
These patterns can signal continuation or reversal and are more significant when they form around key levels. Recognizing these patterns early allows traders to anticipate potential moves and position their trades for optimal entry and exit points.
Risk Management and Key Levels

Effective risk management is crucial when trading key levels. Traders should always set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses if the market moves against their position.
It’s also wise to adjust position sizes based on the volatility and the distance to key levels to manage risk exposure properly. Remember, not all key levels will hold, and being prepared to exit a trade is as important as entering one.
Combining Key Levels with Fundamental Analysis
While key levels provide a technical framework for trading, combining them with fundamental analysis can offer a more holistic view of a stock’s potential.
Understanding a company’s financial health, industry position, and economic factors can complement technical signals and lead to more informed trading decisions.
For instance, a strong earnings report might reinforce the significance of a breakout above a key resistance level, offering additional confidence in the trade.
Incorporating advanced techniques like multiple time frame analysis, price action, and volatility analysis with a solid understanding of risk management and fundamental analysis enriches a trader’s strategy.
By using these methods, traders can better identify and capitalize on key levels in the stock market, enhancing their potential for successful trades.
Why Do Key Levels Matter in Trading?
Key levels matter because they offer a framework for traders to analyze market trends, forecast price movements, and confidently make decisions. They provide insights into market sentiment, showing where buyers and sellers have previously battled over price.
FAQ of How to find key levels in stocks
1. Why should you use key levels in trading?
Using key levels in trading helps identify strategic points for entering and exiting trades, improving the potential for profitability while managing risk.
2. What are key Fibonacci extension levels in trading?
Key Fibonacci extension levels in trading are used to forecast potential areas of interest beyond the current price range. They are often used to set profit targets in trend continuation scenarios.
3. Is it enough to trade financial markets with key levels?
While key levels provide valuable insights, the most successful traders use them with other analysis tools and indicators to make well-rounded trading decisions.
4. How do you find the key zone in trading?
To find the key zone in trading, identify areas where the price has consistently shown support or resistance. Additionally, look for confluences with other indicators, such as volume or moving averages.
5. What are the key levels in stocks?
Key stock levels are price points at which significant price movements are likely to occur. They are identified through historical price action and volume analysis.
6. How do you identify major support and resistance levels?
Identify major support and resistance levels by looking for price points. These are areas where the stock has reversed or paused significantly, often accompanied by high trading volume.
7. What are the most common Key Levels Trading Strategies?
Trading Breakouts with Key Levels. When the price breaks through a key level with significant volume, it can signal the start of a new trend. Trading Reversals with Key Levels. A reversal at a key level, especially when accompanied by high volume or other confirming signals, can indicate a potential change in trend direction.




