
A Comprehensive Guide to the Strat Trading
The Strat trading strategy, developed by Rob Smith, provides a structured approach for traders to navigate various market conditions effectively. It combines technical analysis, market psychology, and rigorous risk management to improve trading decisions and identify high-probability trade opportunities.
What is strat trading?
The Strat is a price action trading strategy that utilizes the full-time frame continuity to analyze and interpret market movements across multiple timeframes. This strategy helps traders understand and apply patterns in price action to predict future market movements reliably.
Key Components of The Strat
- Bar Scenarios: The Strat categorizes market actions into three scenarios:
Inside Bar (Scenario 1)
Represents consolidation. It occurs when the bar’s high and low are within the high and low of the previous bar.
Directional Bar (Scenario 2)
Indicates a clear market direction, either up or down, showing a higher high and higher low or a lower high and lower low.
Outside Bar (Scenario 3)
It occurs when the bar makes both a higher high and a lower low than the previous bar, often signaling a potential broadening formation and a significant market move.
- Multi-Timeframe Analysis: This involves examining charts from multiple timeframes to ensure continuity and consistency in the market’s direction. It helps in identifying stable trends and better trade entry and exit points.
- Pattern Recognition: The Strat emphasizes recognizing continuation patterns and broadening formations to forecast potential market shifts effectively. This requires a keen understanding of candle patterns and their implications on price movement.
How to Identify Trade Opportunities

- Understand Full-Time Frame Continuity: Check if shorter time frames align with longer-term trends to confirm the strength and sustainability of the market movement.
- Spot High Probability Patterns: Use The Strat’s scenarios to identify patterns that suggest a continuation or reversal of trends.
- Technical Analysis Tools: Incorporate tools like RSI for additional confirmation on entry and exit points, ensuring trades align with both momentum and structure shifts.
Trading Plan and Risk Management
Establish Clear Entry and Exit Points: Define precise criteria for entering and exiting trades based on identified patterns and scenarios.
Set Stop Loss Orders: Use stop-loss orders to minimize potential losses, placing them at strategic points that a market structure shift invalidates.
Manage Trade Sizes: Adjust trade sizes based on the risk assessment of each trade to balance potential gains with possible losses.
Ensure each trade decision aligns with both the micro (individual bars and patterns) and macro (full-time frame continuity) views.
Continuously assess the market structure and adjust strategies as new information unfolds through price action and market dynamics.
Understanding Strat Patterns in Trading
One of the crucial elements of Strat trading is the formation of specific chart patterns. Strat trading relies on unique 2-3 candle patterns such as the 2-1-2 and 3-1-2, which are critical for predicting market behavior. Mastering these patterns is essential for anyone looking to excel using the Strat methodology.
Before applying this methodology, you need to familiarize yourself with these formations. Here are some basic Strat candle combinations:
1-2-2 RevStrat Reversal
It starts with an Inside Bar and continues with two consecutive Directional Bars (either 2U or 2D). It indicates a strong reversal, especially if the Directional Bars signal a shift from the previous trend suggested by the Inside Bar.
2-1-2 Pattern
This pattern starts with a Directional Bar (either 2U or 2D). Then it continues with Inside Bar , and concludes with another Directional Bar. The 2-1-2 pattern strongly suggests a potential trend continuation or reversal.
3-1-2 Pattern
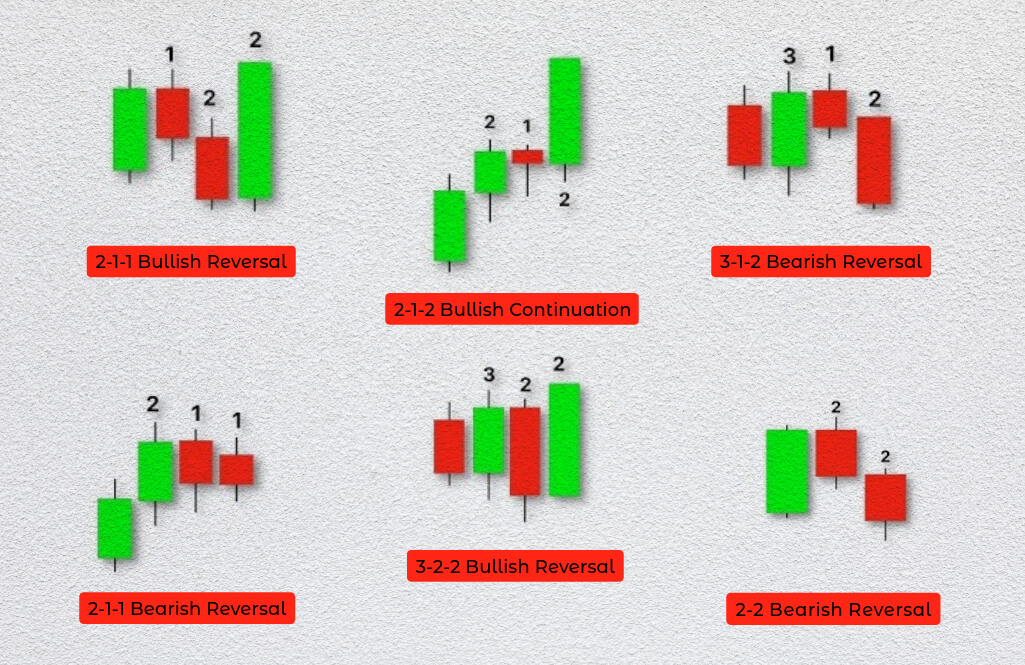
The 3-1-2 pattern includes an Inside Bar, Outside Bar and finishes with a Directional Bar. It is crucial for spotting potential market shifts and broadening formations.
2U-2D Reversal
This pattern starts with an Upward Directional Bar (2U) and is followed by a Downward Directional Bar (2D). It suggests a potential reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend, often reflecting a change in market sentiment.
2D-2D Continuation
Characterized by consecutive Directional Bars Down (2D), this pattern indicates a strong continuation of a downward trend, with each successive 2D bar amplifying the bearish momentum.
3-2U Range Expansion Continuation
Starting with an Outside Bar and followed by an Upward Directional Bar (2U). It shows an upward continuation, especially after a period of consolidation or uncertainty as shown by the Outside Bar.
Forex example
Trading with The Strat strategy in Forex involves understanding the key components of The Strat—bar scenarios, full-time frame continuity, and multiple timeframe analysis. Let’s walk through a step-by-step example of how you might trade using The Strat strategy in the Forex market.
Example: Trading EUR/USD with The Strat
Step 1: Identify the Long-Term Trend
Analyze the Daily Chart: Start by looking at the daily chart of EUR/USD to determine the overall trend. Suppose the trend on the daily chart shows higher highs and higher lows, indicating an uptrend.
Step 2: Check Time frame Continuity
Analyze Shorter Timeframes: Next, check the 4-hour and 1-hour charts to ensure they align with the daily chart’s uptrend. This confirms full-time frame continuity, where all significant timeframes agree on the direction of the market.
Step 3: Spot High-Probability Entry Points
Look for Scenario 2 (Directional Bars): On the 1-hour chart, identify a Scenario 2 situation where a bar closes higher than the previous bar’s high, confirming a continuation of the uptrend.
Confirm with Technical Analysis: Use technical tools such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to check if the market is not in an overbought condition, ensuring the upward momentum is still healthy.
Step 4: Plan Your Trade

Entry Point: Enter a long position at the close of the directional bar that confirms the trend continuation.
Stop Loss: Place a stop loss below the most recent low before your entry point to limit potential losses if the market reverses.
Take Profit: Set a take-profit level at a previous resistance level or use a risk-reward ratio of at least 1:2, locking in potential profits.
Step 5: Manage Your Trade
Adjust Stop Loss: As the price moves in your favor, consider moving the stop loss to break even or using a trailing stop loss to protect your gains.
Monitor for Continuity: Keep an eye on the price action and upcoming economic events that might affect the EUR/USD pair, adjusting your strategy as needed.
Step 6: Review and Adjust
What is the purpose of the strat method in trading
The purpose of using the Strat trading technique is to enhance objective trading by minimizing emotional influences and focusing on market-driven data.
This method primarily examines the relationships between individual candlestick patterns, their alignment with support and resistance levels, and their consistency across various time frames.
It aims to clarify market movements by cutting through market noise, providing traders with an unbiased perspective.
The technique encourages trading decisions based on Strat patterns, devoid of emotional bias. Over time, traders can learn to easily recognize these patterns on price charts, as most Strat patterns are straightforward for professional traders to identify.
Bottom Line
The Strat offers a comprehensive framework that helps traders understand the complexities of financial markets through a systematic approach.
It not only aids in identifying trade opportunities but also emphasizes robust risk management to ensure sustainability in trading. By mastering The Strat, traders can enhance their ability to make informed and disciplined trading decisions across multiple asset classes, including forex and equities.
Traders interested in The Strat should invest time in learning and practicing the different scenarios and patterns, preferably in a simulated trading environment, before applying the strategy in live trading conditions.




