
What Is An Algorithmic Stablecoin – Get All The Information
Have you wondered recently, “What is algorithmic stablecoin, and why is it essential to learn more about it in this industry?” As a passionate trader and investor in this volatile industry, have you been triggered to learn more about the oft-mentioned stablecoins?
If you are interested in a long-term and successful crypto industry career, you must familiarize yourself with the term “Algorithmic stablecoin”.
However, in case you’re an absolute beginner, we should take a step back and clarify what stablecoin represents in the first place, what it is divided into, what it is used for, as well as other indispensable information about it.
What does a stablecoin represent?
A stablecoin represents a specific type of cryptocurrency whose value has to be pegged to a specific reference asset. That asset could be something of the following:
- Exchange-traded commodities like precious metals, for instance,
- Another cryptocurrency
- Fiat money.
These stablecoins include a huge number of purported purposes. Traders are able to utilize them in their everyday trading lives for payments. Theoretically speaking, stablecoins are more likely to keep their value than other extremely volatile cryptos.
On the other hand, in practice, numerous stablecoins didn’t manage to keep their “stable value”. These stablecoins don’t provide interest returns to the holder and are essentially non-interest bearing.
Deriving peg from the collateral of assets
It is crucial to comprehend that stablecoins usually derive their peg from a collateral of assets, i.e. the so-called “underlying reserve”. That reserve might also include some of the following:
- Precious metals
- Fiat currency
- Securities
- Treasuries
- Cash equivalents
- Bonds.
Fiat, commodity, and cryptocurrency-backed.
As mentioned above, stablecoins are either fiat-backed, commodity-backed, or cryptocurrency-backed. Before answering “What is an algorithmic stablecoin”, you should understand each of these backing categories that will help you understand stablecoins even more.
- Fiat-backed stablecoins: These coins are based on the value of the backing currency affiliated with the mediator-regulated financial entity.
- Commodity-backed stablecoins: Their value is pegged to at least one commodity or more.
- Cryptocurrency-backed stablecoins: They are issued with cryptos as collateral, while their supply is regulated on-chain with the utilization of smart contracts.
How do stablecoins work?
To fully understand how stablecoins work, remember that these coins utilize an algorithm to control supply. In addition to that, they might keep reserve assets as collateral via algorithmic formulas that exist to control that supply.
Two crucial types of stablecoins
There are also two types of stablecoins that you should be aware of:
- Algorithmic
- Collateralized
The majority of stablecoins drive their peg from collateral. However, that’s only sometimes the case. Some are called “Algorithmic stablecoins”, while others have other names.
Let’s answer the most frequently asked question regarding stablecoins, “What is an algorithmic stablecoin” first, shall we?
What is algorithmic stablecoin exactly?

Those wondering “What is an algorithmic stablecoin” should understand that algorithmic stablecoins are exclusively pegged to the various assets’ values via smart contracts. That grows or lowers their overall supply established on their present market values.
Once the algorithmic stablecoin is traded above its current peg, that’s the time when these coins are minted, lowering their value. On the other hand, once these algorithmic stablecoins are traded underneath their peg, it’s the time when they are burned, increasing their value.
Algorithmic stablecoins are known not to be using collateral. Instead of that, these types of stablecoins are dependable on smart contracts, yielding unlimited liquidity.
How do algorithmic stablecoins differ from collateralized stablecoins?
On the opposite side of the algorithmic stablecoins, we have collateralized ones. These collateralized stablecoins are burned or minted once assets are withdrawn or deposited to their reserves.
If the collateralized stablecoins are pegged to the USD, for example, the USDC mints for each 1%USD deposited, and one coin gets burned for each USD 1 withdrawn from all their reserves. These stablecoins need liquid assets and those that can be traded fast to answer to all the supply and demand changes.
The main difference between collateralized and algorithmic stablecoins is that collateralized ones are kept stable utilizing collateralized assets. On the other hand, algorithmic stablecoins are still stable using smart contract algorithms.
If we compare these two types, we can see that algorithmic stablecoins are riskier than collateralized ones. Exclusively stablecoins that have reliable collateral are considered obligated to stay.
How do algorithmic stablecoins work?
Since algorithmic stablecoins are considered specific cryptocurrency assets whose value is underpinned by another cryptocurrency asset, it’s crucial to comprehend that they are designed to keep a stable price. They are created by leveraging diverse mechanisms to keep their value.
These mechanisms are documented in the protocol.
It means that anyone can access them publicly on the blockchain. To steer clear of stablecoin de-pegging of the price, the prices of algorithmic stablecoins are closely tied up to the present market conditions. Understanding that this type of coin’s goal is to achieve a stable value, in general, is crucial.
Pegging vs Depegging
For complete newbies in the crypto industry, we’d like to explain Pegging vs debugging and its main differences. First, Pegging stands for a strive to set a fixed exchange rate between two different currencies.
On the other hand, depegging means that a particular stablecoin value is decreasing underneath the fixed exchange rate and ultimately, depending, spells “disaster” regarding stablecoin.
Different types of algorithmic stablecoins
There are different types of algorithmic stablecoins that we’ll cover and that you need to know:
- Fractional-algorithmic
- Seigniorage
- Rebase
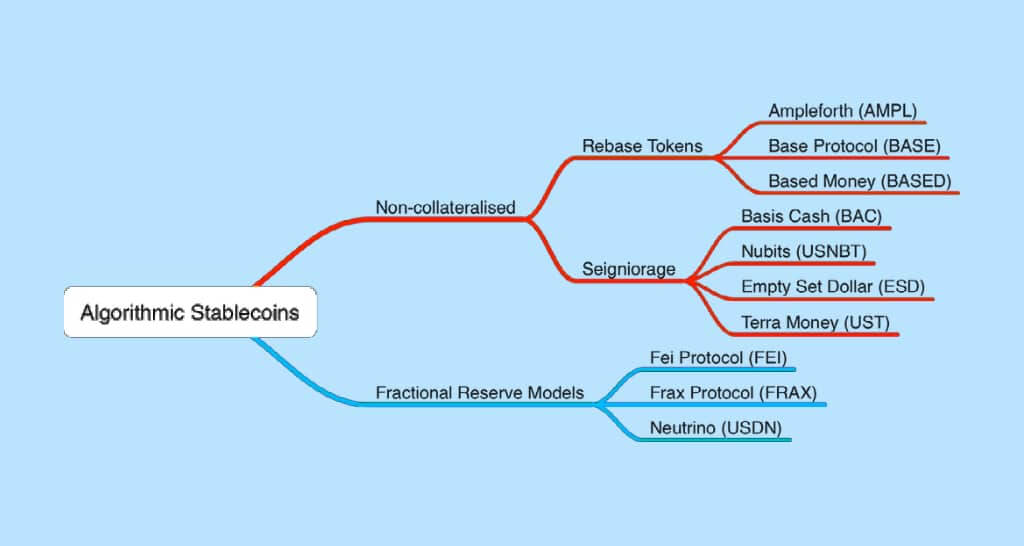
Fractional
This type of Fractional-algorithmic coin represents a specific combination of the rebase and seigniorage stablecoins. Its main goal is to keep the value of a stablecoin via being moderately backed by fiat, i.e. collateral currency and including an algorithm that alters the stablecoin supply. The pioneer of the fractional coin is Frax Finance.
Seigniorage
Seigniorage algorithmic stablecoins use the so-called multi-coins system. In this situation, a particular stablecoin is established to be stable, and at the minimum, one other coin is created to ease such stability.
This model of stablecoins typically applies to mint-and-burn mechanisms that are protocol-based and free market mechanisms.
Rebase
Rebase algorithmic stablecoins manipulate the base supply to keep its peg. The protocol usually mints or burns coins from circulation. That depends on the stablecoin’s price deviation from 1 USD.
Once the price is above 1 USD, minting will happen, while burning will happen when the price is underneath 1 USD.
How to measure algorithmic stablecoins?

Besides getting the proper answer to “What is an algorithmic stablecoin”, knowing how to measure them is crucial. It means comprehending all the essential factors that impact the effectiveness of stablecoins and metrics that estimate their overall performance.
If you are eager to determine their effectiveness, here is what you need to know:
- Incentives
- Governance
- Token adoption rate
Incentives
Regarding incentives, certain algorithmic stablecoins do rebase mechanisms in order to motivate traders. All these mechanisms adjust the total supply of tokens in circulation, which doesn’t include changing the token value.
On the opposite side, there are various other protocols that either benefit or reward for taking part in alternative investments. Might be:
- Adding supply/demand matching
- Burning coupons.
Governance
The majority of algorithmic stablecoins could be found as DAO, i.e. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations. However, only some of them are able to show an active group that’s frequently implementing upgraded proposals.
In addition, smart contract governance is a great pick for an algorithmic stablecoin. Ensuring legitimate token distribution, in addition to governance rights offered to each stakeholder, is crucial.
Also, keep in mind that some algorithmic stablecoins have begun following centralized governance.
What are the main pros and cons?
The main pros
- Having more stability than any other asset currently on the market
- Much easier to obtain numerous crypto asset exchanging platforms
- An investment that’s eligible for beginners and professionals as well.
On the other hand, we have cons such as:
- Not being supported by the real assets
- Provisory on demand for keeping the particular value
- There is no guarantee of price stability for keeping the true value.
What are the most famous algorithmic stablecoins?
Here is the list of the most famous algorithmic stablecoins that you need to know:
- TerraUSD (UST): It is supported by the famous LUNA (Terra). 1 UST is able to be minted by burning the same amount of LUNA: 1 US$ LUNA = 1 UST
- DAI: Ethereum-based stablecoin whose price is pegged to the US$.
Conclusion
In the crypto industry, algorithmic stablecoins have emerged as a unique and innovative solution. These digital assets combine the stability of a traditional stablecoin with the flexibility of another supporting crypto asset. It all creates a powerful financial tool.
By relying on an algorithm or smart contract to govern the relationship between these two tokens, algorithmic stablecoins can adjust and adapt to changing market conditions, maintaining a stable value while still providing growth potential.
As the crypto market continues to evolve, algorithmic stablecoins are undoubtedly an exciting and dynamic part of the landscape.
FAQ

What does a stablecoin represent?
A stablecoin represents a specific type of cryptocurrency whose value has to be pegged to a specific reference asset. Stablecoins are either fiat-backed, commodity-backed, or cryptocurrency-backed.
What is an algorithmic stablecoin?
Algorithmic stablecoins are exclusively pegged to the various assets’ values via smart contracts. That grows or lowers their overall supply established on their present market values. That grows or lowers their overall supply established on their present market values.
What are the different types of stablecoins?
There are different types of algorithmic stablecoins that we’ll cover and that you need to know:
- Fractional-algorithmic
- Seigniorage
- Rebase
How to measure algorithmic stablecoins?
If you are eager to determine their effectiveness, here is what you need to know:
- Incentives
- Governance
- Token adoption rate
What is the difference between collateralized and algorithmic stablecoins?
The main difference between collateralized and algorithmic stablecoins is that collateralized ones are kept stable utilizing collateralized assets. On the other hand, algorithmic stablecoins are still stable using smart contract algorithms.
If we compare these two types, we can see that the second one is riskier than the collateralized ones. Exclusively stablecoins that have reliable collateral are considered obligated to stay.
What are the main pros of algorithmic stablecoins?
- Having more stability than any other asset currently on the market
- Much easier to obtain numerous crypto asset exchanging platforms
- An investment that’s eligible for beginners and professionals as well.
What are the main cons of algorithmic stablecoins?
- Not being supported by the real assets
- Provisory on demand for keeping the particular value
- There is no guarantee of price stability for keeping the true value.
What are the most popular algorithmic stablecoins?
- TerraUSD (UST): It is supported by the famous LUNA (Terra). 1 UST is able to be minted by burning the same amount of LUNA: 1 US$ LUNA = 1 UST
- DAI: Ethereum-based stablecoin whose price is pegged to the US$.




